2015-12-13 10:46:24 +00:00
|
|
|
# PowerDNS-Admin
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2018-04-01 09:07:41 +00:00
|
|
|
A PowerDNS web interface with advanced features.
|
2018-09-07 07:58:16 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-12-09 21:42:53 +00:00
|
|
|
[](https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin/actions/workflows/codeql-analysis.yml)
|
2022-12-09 21:57:13 +00:00
|
|
|
[](https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin/actions/workflows/build-and-publish.yml)
|
2015-12-13 10:46:24 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2015-12-13 11:07:10 +00:00
|
|
|
#### Features:
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides forward and reverse zone management
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides zone templating features
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides user management with role based access control
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides zone specific access control
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides activity logging
|
|
|
|
|
- Authentication:
|
|
|
|
|
- Local User Support
|
|
|
|
|
- SAML Support
|
|
|
|
|
- LDAP Support: OpenLDAP / Active Directory
|
|
|
|
|
- OAuth Support: Google / GitHub / Azure / OpenID
|
|
|
|
|
- Two-factor authentication support (TOTP)
|
|
|
|
|
- PDNS Service Configuration & Statistics Monitoring
|
2016-06-21 22:22:02 +00:00
|
|
|
- DynDNS 2 protocol support
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
- Easy IPv6 PTR record editing
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides an API for zone and record management among other features
|
|
|
|
|
- Provides full IDN/Punycode support
|
2015-12-13 11:07:10 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
## Running PowerDNS-Admin
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
There are several ways to run PowerDNS-Admin. The quickest way is to use Docker.
|
|
|
|
|
If you are looking to install and run PowerDNS-Admin directly onto your system, check out
|
|
|
|
|
the [Wiki](https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin/wiki#installation-guides) for ways to do that.
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Docker
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-12-09 22:03:46 +00:00
|
|
|
Here are two options to run PowerDNS-Admin using Docker.
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
To get started as quickly as possible, try option 1. If you want to make modifications to the configuration option 2 may
|
|
|
|
|
be cleaner.
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Option 1: From Docker Hub
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To run the application using the latest stable release on Docker Hub, run the following command:
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
$ docker run -d \
|
2021-05-07 21:40:54 +00:00
|
|
|
-e SECRET_KEY='a-very-secret-key' \
|
2020-09-16 06:43:41 +00:00
|
|
|
-v pda-data:/data \
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
-p 9191:80 \
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
powerdnsadmin/pda-legacy:v0.3.0
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
```
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This creates a volume named `pda-data` to persist the default SQLite database with app configuration.
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### Option 2: Using docker-compose
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2021-05-07 21:40:54 +00:00
|
|
|
1. Update the configuration
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
Edit the `docker-compose.yml` file to update the database connection string in `SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI`.
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
Other environment variables are mentioned in
|
|
|
|
|
the [legal_envvars](https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin/blob/master/configs/docker_config.py#L5-L46).
|
|
|
|
|
To use the Docker secrets feature it is possible to append `_FILE` to the environment variables and point to a file
|
|
|
|
|
with the values stored in it.
|
|
|
|
|
Make sure to set the environment variable `SECRET_KEY` to a long random
|
|
|
|
|
string (https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/config/#SECRET_KEY)
|
2020-04-20 22:23:57 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Start docker container
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
$ docker-compose up
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You can then access PowerDNS-Admin by pointing your browser to http://localhost:9191.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Screenshots
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2018-08-14 02:36:26 +00:00
|
|
|
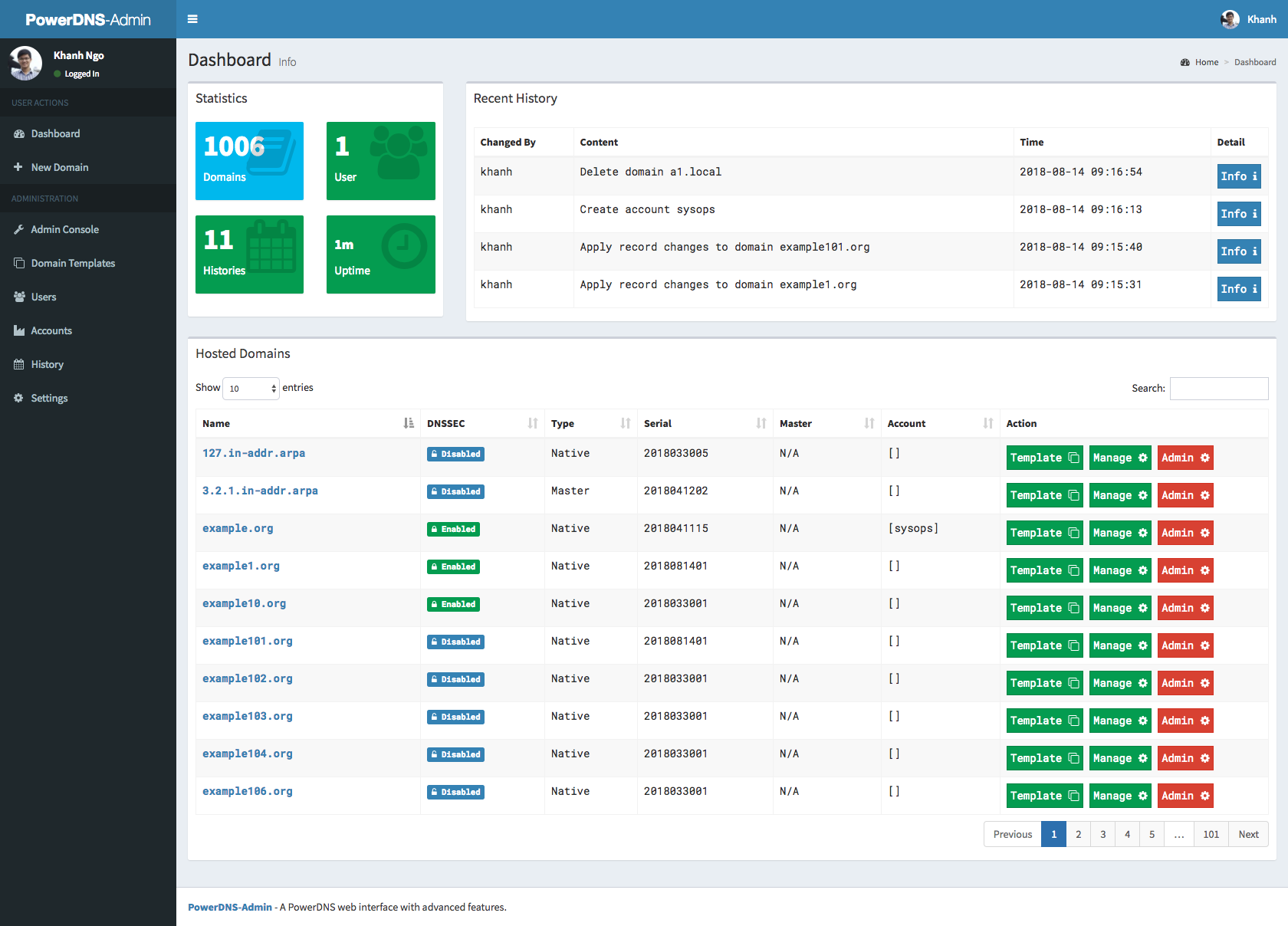
|
2020-05-17 07:37:15 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## LICENSE
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-02-26 08:47:28 +00:00
|
|
|
This project is released under the MIT license. For additional
|
|
|
|
|
information, [see here](https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin/blob/master/LICENSE)
|